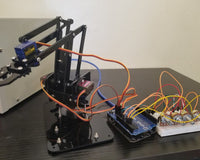
Overview
Indoor gardening and plant care have grown popular, especially for urban dwellers with limited outdoor space. One common issue, however, is forgetting to water plants on time. This project demonstrates how to build a Smart Plant Monitor using the WeMos D1 Mini (ESP12 Wi-Fi Development Board) that automatically detects soil moisture and waters the plant.
We created two versions of this project so users can choose what display works best for them:
Version 1: Smart Plant Monitor with OLED + Auto Watering
(Using OLED Display & L298N Motor Driver)
This version uses an OLED display (128x64) to show clear text and expressive emoji faces, making it easier to monitor the plant’s soil condition at a glance. It provides detailed visual feedback, which is ideal for users who prefer readable information. The L298N motor driver allows more control over the water pump, including speed adjustments through PWM (Pulse Width Modulation). This setup is more flexible, allowing for smoother motor operation and better water flow control. 
Version 2: Smart Plant Monitor with 8x8 Matrix LED + Auto Watering
(Using 8x8 LED Matrix & Relay Module)
This version introduces a Matrix LED (8x8) display, offering a more playful and engaging way of monitoring plant health. Instead of typical text, it shows pixel-style emojis—a smiley for moist soil and a sad face for dry which gives the system personality and charm. It's especially eye-catching for educational, hobbyist, or demo environments. The use of a relay module simplifies motor control to a basic ON/OFF function, making this version easier to build. 
Hardware Used
- WeMos D1 Mini (ESP12)
- Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor
- SX1308 Step-Up DC-DC Converter
-
L298N Motor Driver Board Module ( MOSFET) - ( For Version 1)
-
OLED Display module 128x64 0.96-inch, white I2C - ( For Version 1)
- Matrix LED 8x8 Display (MAX7219) - ( For Version 2)
- Relay Module (2-Channel, 5V) - ( For Version 2)
-
DC Water Pump (12V R385 Diaphragm)
- Dupont Jumper Wires (M-M / F-F)
- Breadboard (830 tie points)
Software Used
- Arduino IDE 2.3.6
-
Fritzing
Application Discussion
WeMos D1 Mini (ESP12)
The WeMos D1 Mini is a compact microcontroller board based on the ESP8266 Wi-Fi chip. It features digital I/O pins, built-in Wi-Fi capability, and is programmable using the Arduino IDE. Its small size makes it ideal for IoT and automation projects.
Pinout:

Application:
In this project, the WeMos D1 Mini acts as the brain of the system. It reads data from the soil moisture sensor, controls the relay to turn the water pump on or off, and sends display commands to the LED matrix for user feedback.
Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor
This sensor detects the moisture content of soil by measuring changes in capacitance. It outputs an analog voltage that varies depending on how wet or dry the soil is. Unlike resistive sensors, it’s corrosion-resistant and more durable over time.

Pinout:
Application:
The sensor constantly monitors the soil’s condition and sends analog data to the WeMos D1 Mini. The microcontroller interprets this data and determines whether the plant needs watering based on a predefined moisture threshold.
SX1308 Step-Up DC-DC Converter
The SX1308 is a boost converter module that increases a lower input voltage to a higher output. It can be adjusted to deliver up to 28V and is known for its efficiency and compact size. It’s commonly used in battery-powered projects requiring higher voltage.

Application:
This converter boosts the 5V input from the system to 12V to power the DC water pump. It ensures that the pump operates efficiently even when the system is powered through USB or a low-voltage source. However, if you're using a 5V pump, you don't need the converter anymore — this makes the wiring simpler and helps save battery or power.
OLED Display Module (128x64, 0.96-inch, White, I2C)
A lightweight graphical display module with high contrast and low power usage. It uses I2C communication, requiring only two pins (SCL & SDA).
Pinout:
Application:
Displays real-time plant moisture status, such as visual emojis (happy/sad face) based on moisture readings. It is ideal for minimal wiring and clear data display.
NOTE: This is the display module for Version 1.
Matrix LED 8x8 Display (MAX7219)
The 8x8 LED Matrix display with MAX7219 driver is used to show simple graphics or icons. It is controlled through SPI communication and supports brightness adjustment and multiple modules in cascade. This display is fun, engaging, and energy efficient.

Pinout:
Application:
In the system, the LED matrix displays a smiling face when the plant is well-watered and a sad face when it is dry. It provides a creative and emotional visual cue to users, especially useful in environments where reading text is impractical.
NOTE: This is the display module for Version 2.
Relay Module (2-Channel, 5V)
A relay module is an electrically operated switch that allows a microcontroller to control high-voltage devices. This 2-channel version can independently switch two separate circuits. It uses opto-isolation for added safety and reliability.

Application:
The relay module allows the D1 Mini to safely control the 12V water pump. When the soil is dry, the relay activates the pump to deliver water, then turns it off automatically after a set time.
L298N Motor Driver Board Module (Alternative to MOSFET)
A dual H-Bridge motor driver that can control two DC motors or one motor with directional control. Accepts 5V logic and up to 35V motor power input.
Application:
Can be used in place of a relay to drive the water pump. Allows for finer motor control, including direction and PWM speed control if needed. Useful if you plan to expand or regulate water flow rate.
DC Water Pump (12V R385 Diaphragm)
This mini diaphragm pump is a small, 12V-powered device designed to move water at low pressure. It is ideal for small irrigation systems and projects requiring automatic water delivery. It has low noise and power consumption.
Application:
The pump waters the plant whenever the soil moisture is below the set threshold. It is automatically controlled by the relay or the L298N motor driver and powered by the boosted 12V output from the DC-DC converter, making plant care more convenient and hands-free.
Hardware Setup (version 1)

Hardware Setup (version 2)

Software Setup (version 1)
Source Code:
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
#include <Adafruit_SSD1306.h>
// OLED display size
#define SCREEN_WIDTH 128
#define SCREEN_HEIGHT 64
#define OLED_RESET -1
Adafruit_SSD1306 display(SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT, &Wire, OLED_RESET);
// Pin definitions
#define SOIL_SENSOR_PIN 16 // D0 on Wemos D1 Mini (A0 is GPIO17, but you use GPIO16 here)
#define ENA_PIN 15 // PWM pin for motor speed control (GPIO15)
#define IN1_PIN 13 // Motor direction control pin 1 (GPIO13)
#define IN2_PIN 12 // Motor direction control pin 2 (GPIO12)
#define MOISTURE_THRESHOLD 1000 // Threshold for dry soil
bool motorActivated = false; // State to prevent repeated watering cycles
void drawFace(int x, int y, int mood) {
// Draw circular face
display.drawCircle(x, y, 20, SSD1306_WHITE); // Face outline
display.fillCircle(x - 6, y - 6, 4, SSD1306_WHITE); // Left eye
display.fillCircle(x + 6, y - 6, 4, SSD1306_WHITE); // Right eye
if (mood == 1) { // Happy face (Wet)
display.drawLine(x - 7, y + 8, x - 3, y + 10, SSD1306_WHITE);
display.drawLine(x - 3, y + 10, x + 3, y + 10, SSD1306_WHITE);
display.drawLine(x + 3, y + 10, x + 7, y + 8, SSD1306_WHITE);
} else { // Sad face (Dry)
display.drawLine(x - 7, y + 10, x - 3, y + 8, SSD1306_WHITE);
display.drawLine(x - 3, y + 8, x + 3, y + 8, SSD1306_WHITE);
display.drawLine(x + 3, y + 8, x + 7, y + 10, SSD1306_WHITE);
}
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Initialize OLED
if (!display.begin(SSD1306_SWITCHCAPVCC, 0x3C)) {
Serial.println(F("SSD1306 allocation failed"));
for (;;); // Halt
}
display.clearDisplay();
display.display();
// Initialize pins
pinMode(SOIL_SENSOR_PIN, INPUT);
pinMode(ENA_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN1_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN2_PIN, OUTPUT);
// Ensure motor is off at start
digitalWrite(IN1_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN2_PIN, LOW);
analogWrite(ENA_PIN, 0);
}
void loop() {
// Read soil moisture sensor
int soilValue = analogRead(SOIL_SENSOR_PIN);
Serial.print("Soil sensor value: ");
Serial.println(soilValue);
// --- OLED Display Update ---
display.clearDisplay();
if (soilValue > MOISTURE_THRESHOLD) {
// Dry soil detected
drawFace(100, 32, 0); // Sad face on right side
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setTextColor(SSD1306_WHITE);
display.setCursor(10, 10);
display.println("Dry");
display.setCursor(10, 30);
display.println("Soil");
} else {
// Wet soil detected
drawFace(100, 32, 1); // Happy face on right side
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setTextColor(SSD1306_WHITE);
display.setCursor(10, 10);
display.println("Wet");
display.setCursor(10, 30);
display.println("Soil");
}
display.display();
// --- Motor Control Logic ---
if (soilValue > MOISTURE_THRESHOLD) {
if (!motorActivated) {
Serial.println("Motor ON - Watering for 5 seconds");
digitalWrite(IN1_PIN, HIGH);
digitalWrite(IN2_PIN, LOW);
analogWrite(ENA_PIN, 125); // Approx 49% speed
delay(5000); // Water for 5 seconds
// Turn motor off
digitalWrite(IN1_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN2_PIN, LOW);
analogWrite(ENA_PIN, 0);
motorActivated = true;
Serial.println("Motor OFF after watering");
} else {
Serial.println("Soil still dry, motor already activated. No action.");
}
} else {
if (motorActivated) {
Serial.println("Soil moist detected. Resetting motor activation flag.");
motorActivated = false;
} else {
Serial.println("Soil moist, motor remains off.");
}
// Ensure motor is off
digitalWrite(IN1_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN2_PIN, LOW);
analogWrite(ENA_PIN, 0);
}
delay(2000); // Delay before next reading
}
Software Setup (version 2)
include <ledcontrol.h></ledcontrol.h>
// Pin definitions for your LED matrix wiring
#define DIN_PIN 15 // D8 (GPIO15)
#define CS_PIN 13 // D7 (GPIO13)
#define CLK_PIN 12 // D6 (GPIO12)
// Capacitive soil sensor analog input pin
#define SOIL_SENSOR_PIN 16 // D0 (GPIO16)
LedControl lc = LedControl(DIN_PIN, CLK_PIN, CS_PIN, 1);
// Smiley face pattern
byte smiley[8] = {
0b00111100,
0b01000010,
0b10100101,
0b10000001,
0b10100101,
0b10011001,
0b01000010,
0b00111100
};
// Sad face pattern
byte sad[8] = {
0b00111100,
0b01000010,
0b10100101,
0b10000001,
0b10011001,
0b10100101,
0b01000010,
0b00111100
};
// Pin definitions
const int relay1Pin = 0; // D3 (GPIO0) to relay input 1
const int relay2Pin = 2; // D4 (GPIO2) to relay input 2
// Threshold for dry soil detection (adjust based on your sensor calibration)
const int dryThreshold = 1000; // example threshold for analog reading (0-1023)
// State variable to prevent repeated activation
bool motorActivated = false;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(relay1Pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(relay2Pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(SOIL_SENSOR_PIN, INPUT);
lc.shutdown(0, false); // Wake up MAX7219
lc.setIntensity(0, 8); // Set brightness (0-15)
lc.clearDisplay(0); // Clear display
// Initialize relays off (assuming LOW activates relay, so HIGH means off)
digitalWrite(relay1Pin, HIGH);
digitalWrite(relay2Pin, HIGH);
delay(2000); // Wait for sensor stabilization
}
void displayFace(byte face[8]) {
for (int row = 0; row < 8; row++) {
lc.setRow(0, row, face[row]);
}
}
void loop() {
int soilValue = analogRead(SOIL_SENSOR_PIN); // Read soil moisture sensor
Serial.print("Soil sensor analog value: ");
Serial.println(soilValue);
// Display sad face if soil is dry (value >= threshold), else smiley face
if (soilValue >= dryThreshold) {
displayFace(sad);
} else {
displayFace(smiley);
}
// Relay control logic
if (soilValue >= dryThreshold) {
// Soil is dry
if (!motorActivated) {
Serial.println("Soil dry detected. Activating motor for 5 seconds.");
digitalWrite(relay1Pin, LOW); // Activate relay 1 (motor ON)
digitalWrite(relay2Pin, LOW); // Activate relay 2 if needed
delay(5000); // Keep motor ON for 5 seconds
digitalWrite(relay1Pin, HIGH); // Deactivate relay 1 (motor OFF)
digitalWrite(relay2Pin, HIGH); // Deactivate relay 2
motorActivated = true; // Prevent repeated activation
Serial.println("Motor deactivated after 5 seconds.");
} else {
Serial.println("Soil still dry, motor already activated. No action.");
}
} else {
// Soil is wet
if (motorActivated) {
Serial.println("Soil moist detected. Resetting motor activation flag.");
motorActivated = false; // Reset flag to allow future activation
} else {
Serial.println("Soil moist, motor remains off.");
}
digitalWrite(relay1Pin, HIGH); // Ensure relay is off
digitalWrite(relay2Pin, HIGH);
}
delay(2000); // Wait before next reading
}
Code Breakdown
Version 1
Libraries Used:
- Wire.h – Enables I2C communication (used by OLED).
- Adafruit_GFX.h – Core graphics library for displays.
- Adafruit_SSD1306.h – Specific library for controlling OLED (SSD1306)
OLED Display Setup:
#define SCREEN_WIDTH 128
#define SCREEN_HEIGHT 64
#define OLED_RESET -1
- Initializes a 128x64 OLED display with no reset pin.
Moisture Threshold:
#define MOISTURE_THRESHOLD 1000
- When the analog soil reading exceeds 1000, the soil is considered dry.
drawFace() Function:
- Draws a simple smiley or sad face depending on soil moisture.
- Used to add a fun, emotional touch to plant health feedback.
setup() Function:
- Initializes serial communication, OLED display, and motor pins.
- Ensures the motor is off at startup.
loop() Function:
- Reads soil sensor value.
- Displays either "Dry Soil 😢" or "Wet Soil 😊" on the OLED.
- If dry and motor hasn't yet run:
- Activates motor (5 seconds) using L298N and PWM.
- If wet, resets motor state and ensures it's off.
Version 2
Library Used:
- LedControl.h – Used to control MAX7219-based 8x8 LED matrix modules.
Pin Definitions:
#define DIN_PIN 15
#define CS_PIN 13
#define CLK_PIN 12
#define SOIL_SENSOR_PIN 16
const int relay1Pin = 0;
const int relay2Pin = 2;
- DIN, CS, CLK – Communication pins to control the LED matrix.
- relay1Pin/relay2Pin – Connected to relays that activate the water pump.
Smiley & Sad Face Arrays:
byte smiley[8] = { ... };
byte sad[8] = { ... };
- These binary arrays define how the emoji faces are drawn on the 8x8 matrix.
setup() Function:
Initializes:
- Serial communication
- Relay pins (off by default)
- Soil sensor
- LED matrix (brightness and clearing display)
loop() Function:
- Reads soil moisture sensor value.
- Displays a smiley or sad face on the matrix.
- If soil is dry and motor not yet triggered:
- Activates relay for 5 seconds to water the plant.
- Then turns motor off and sets a flag.
- If soil becomes moist again, the motor flag resets for future activation.
Video Demonstration
Version 1: Smart Plant Monitor with OLED + Auto Watering
Version 2: Smart Plant Monitor with 8x8 Matrix LED + Auto Watering
Conclusion
The Smart Plant Monitor with Auto Watering System showcases a practical and creative approach to automating plant care through real-time soil monitoring and automatic watering. This project not only helps maintain healthy plants but also introduces users to essential IoT and automation concepts.
Two versions of the system were developed to suit different preferences and component availability. Version 1 uses an OLED Display and L298N Motor Driver, offering a clean, compact, and beginner-friendly interface with the added benefit of precise motor control via PWM. It provides clear, readable feedback and a more advanced level of customization which is perfect for users who value detail and control.
On the other hand, Version 2 uses an 8x8 Matrix LED and Relay Module, adding a fun and charming twist by displaying expressive pixel-style emojis to indicate plant mood. It offers a more engaging and visually appealing experience, especially suited for hobbyists, students, and quick builds where simplicity is key.
Both versions provide an accessible, practical solution for maintaining healthy plants—especially useful for users who may forget or be too busy to water their plants on time. The system promotes smart gardening and introduces users to IoT and automation principles through hands-on experience.
References
- YouTube – "Soil Moisture Sensor with Wemos D1 Mini and Relay"
- YouTube – "MAX7219 8x8 LED Matrix with Arduino – Smiley Face Display Tutorial"
- CreateLabz Internal Resources and Component Datasheets
- Adafruit OLED and GFX Libraries
- LedControl Library Documentation
- ESP8266/ESP-12 Module Documentation
- Arduino IDE Official Documentation