A potentiometer takes an input voltage and outputs a variable amount of it to a circuit, which is determined by the position of a slider on a resistive element. The potentiometer can be used as a voltage regulator, as described above, a means of introducing a variable amount of resistance into a circuit or as a means of adjusting the power in a circuit. The last case, it is filling the role of a rheostat. These inputs take a voltage (from 0 to 5 volts) and convert it to a digital number between 0 (0 volts) and 1023 (5 volts) (10 bits of resolution).
Hardware Used:
- 1 – LED
You can buy all this Hardware at Createlabz.
Software Used:
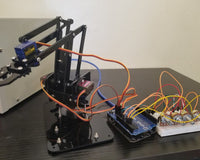
Set up the Hardware:

Code:
/*
Analog Input
Demonstrates analog input by reading an analog sensor on analog pin 0 and
turning on and off a light emitting diode(LED) connected to digital pin 13.
The amount of time the LED will be on and off depends on the value obtained
by analogRead().
The circuit:
- potentiometer
center pin of the potentiometer to the analog input 0
one side pin (either one) to ground
the other side pin to +5V
- LED
anode (long leg) attached to digital output 13
cathode (short leg) attached to ground
- Note: because most Arduinos have a built-in LED attached to pin 13 on the
board, the LED is optional.
created by David Cuartielles
modified 30 Aug 2011
By Tom Igoe
This example code is in the public domain.
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/AnalogInput
*/
int sensorPin = A0; // select the input pin for the potentiometer
int ledPin = 13; // select the pin for the LED
int sensorValue = 0; // variable to store the value coming from the sensor
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// read the value from the sensor:
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
// turn the ledPin on
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
// stop the program for <sensorValue> milliseconds:
delay(sensorValue);
// turn the ledPin off:
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
// stop the program for for <sensorValue> milliseconds:
delay(sensorValue);
}
Code Breakdown:
int sensorPin = A0; int ledPin = 13;
Pins for the Potentiometer and LED.
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
declares the ledPin as an OUTPUT
analogRead()
it will map input voltages between 0 and 5 volts into integer values between 0 and 1023.
digitalWrite()
If the pin has been configured as an OUTPUT with pinMode(), its voltage will be set to the corresponding value: 5V (or 3.3V on 3.3V boards) for HIGH, 0V (ground) for LOW.
Try MORE!!!!
Threshold Switching:
If you want to switch an output when value exceeds certain threshold. Change the loop code to.
void loop() {
int threshold = 512;
if(analogRead(SensorPin) > threshold) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);}
else{ digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);}
}
Fading:
To control the brightness of a LED directly from the potentiometer. To do this we need to first change the pin LED from pin 13 to pin 9.
int ledPin = 13; -----> int ledPin = 9;
and change the loop code to.
void loop() {
int value = analogRead(potPin) / 4;
analogWrite(ledPin, value);
}
then upload the code and watch as the led fades in relation to your potentiometer twisting.
The post Arduino Starter’s Guide (7/7): Potentiometer and LED appeared first on CreateLabz.